PFDEP - Project File Dependencies
Project managers, such as the UNIX utility make, are used to maintain large software projects made up from many components. Users write a project file specifying which components (called tasks) depend on others and the project manager can automatically update the components in the correct order.
Problem
Write a program that reads a project file and outputs the order in which the tasks should be performed.
Input
For simplicity we represent each task by an integer number from 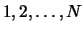 (where
(where 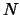 is the total number of tasks). The first line of input specifies the number
is the total number of tasks). The first line of input specifies the number 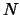 of tasks and the number
of tasks and the number 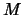 of rules, such that
of rules, such that 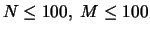 .
.
The rest of the input consists of 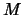 rules, one in each line, specifying dependencies using the following syntax:
rules, one in each line, specifying dependencies using the following syntax:
This rule means that task number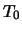
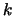

...

Note that tasks numbers are separated by single spaces and that rules end with a newline. Rules can appear in any order, but each task can appear as target only once.
Your program can assume that there are no circular dependencies in the rules, i.e. no task depends directly or indirectly on itself.
Output
The output should be a single line with the permutation of the tasks 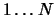 to be performed, ordered by dependencies (i.e. no task should appear before others that it depends on).
to be performed, ordered by dependencies (i.e. no task should appear before others that it depends on).
To avoid ambiguity in the output, tasks that do not depend on each other should be ordered by their number (lower numbers first).
Example
Input: 5 4 3 2 1 5 2 2 5 3 4 1 3 5 1 1 Output: 1 5 3 2 4
--------------------------------------------EDITORIAL-----------------------------------------------
QUEUE IMPLEMENTATION OF TOPOLOGICAL SORT WILL BE EASY TO USE IN THIS PROBLEM
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int>li[1000000];
int vis[1000000];
vector<int> ans;
int n,m;
int deg[1000000];
struct compare
{
bool operator() (const int& l, const int& r)
{
return l>r;
}
};
int toposort()
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, compare > q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(deg[i]==0)
{
q.push(i);
//ans.push_back(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int node=q.top();
ans.push_back(node);
q.pop();
vis[node]=1;
vector<int>:: iterator it;
for(it=li[node].begin();it!=li[node].end();it++)
{
if(deg[*it]!=0)
{
deg[*it]--;
if(deg[*it]==0)
{
//cout<<" push "<<*it<<endl;
// ans.push_back(*it);
q.push(*it);
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int st,k;
cin>>st>>k;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++)
{
int a;
cin>>a;
li[a].push_back(st);
deg[st]++;
}
}
toposort();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
No comments:
Post a Comment